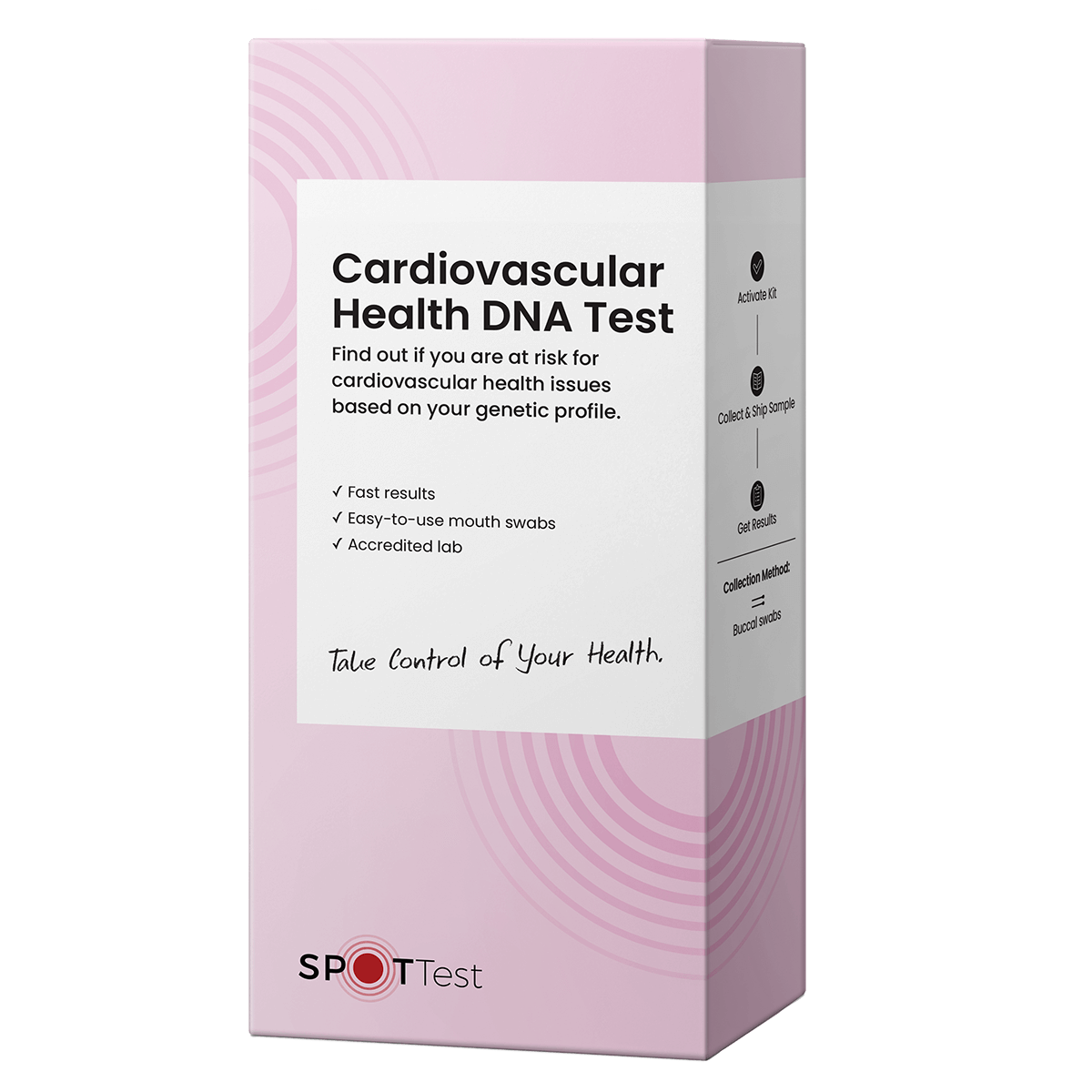
Cardiovascular Health Risk DNA Test
Find out if you are at risk for cardiovascular health issues based on your genetic profile.
Measures:
- Genetic variants associated with lipid levels, including cholesterol and triglycerides.
Collection methods:
Buccal swabs
$349.00
- Discreet shipping
- Accredited lab
- Secure Online Results
- Highest accuracy
- Discreet
- Results in 1-3 business days
About the test
Understanding Your Genetic Risk for Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular disease encompasses a variety of conditions, many of which involve the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels, leading to issues such as chest pain (angina), heart attacks, and strokes. These diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for over 30% of all fatalities. While lifestyle factors like lack of exercise, poor diet, and smoking contribute significantly to heart disease risk, genetic factors can also play a key role. Certain inherited genetic variants may predispose you to heart conditions, even if you follow a healthy lifestyle.
By providing a simple mouth swab, this test can reveal whether you carry genetic variants that could impact your heart health, helping you take proactive steps toward prevention.
Genetic Profile
Genetic Variants and Cardiovascular Disease Risk
There are various genetic variants associated with cardiovascular disease, with some increasing the risk and others offering a protective effect.
-
ANGPTL4, APOA5, FADS1, GALNT2, HNF4A, LIPG, MMAB
Reduced “good” HDL-cholesterol -
CETP, LCAT, LIPC, LPL
Elevated “good” HDL-cholesterol -
APOB, FADS1, LDLR, NCAN, PCSK9, SORT1, SUGP1
Reduced “bad” LDL-cholesterol -
HMGCR, HNF1A, TRIB1
Elevated “bad” LDL-cholesterol -
LPA
Elevated lipoprotein(a) -
CRP, GCKR
Elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) -
APOA5, FADS1, GALNT2, GCKR, NOS3, TRIB1
Elevated triglycerides -
ANGPTL3, LPL, MLXIPL, NCAN
Reduced triglycerides -
9p21
Decreased control of cell proliferation
- Cholesterol: A fatty substance produced by the body and found in certain foods. It is carried in the bloodstream by HDL (good cholesterol) and LDL (bad cholesterol). Low HDL or high LDL can cause cholesterol to build up in the arteries, narrowing or blocking blood vessels.
- Triglycerides: The fat in your body that comes from digesting food. High levels of triglycerides can lead to obesity and increase the risk of heart disease.
- C-reactive protein (CRP): A protein produced by the liver that rises during inflammation. Elevated CRP levels can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Lipoprotein(a): A type of lipoprotein similar to LDL, containing cholesterol. High levels of lipoprotein(a) can elevate the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Genes Analyzed in This Cardiovascular Health Test
-
ANGPTL4, APOA5, FADS1, GALNT2, HNF4A, LIPG, MMAB
Reduced “good” HDL-cholesterol -
CETP, LCAT, LIPC, LPL
Elevated “good” HDL-cholesterol -
APOB, FADS1, LDLR, NCAN, PCSK9, SORT1, SUGP1
Reduced “bad” LDL-cholesterol -
HMGCR, HNF1A, TRIB1
Elevated “bad” LDL-cholesterol -
LPA
Elevated lipoprotein(a) -
CRP, GCKR
Elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) -
APOA5, FADS1, GALNT2, GCKR, NOS3, TRIB1
Elevated triglycerides -
ANGPTL3, LPL, MLXIPL, NCAN
Reduced triglycerides -
9p21
Decreased control of cell proliferation
Factors that Affect Your Cardiovascular Health
- Cholesterol: A fatty substance produced by the body and found in certain foods. It is carried in the bloodstream by HDL (good cholesterol) and LDL (bad cholesterol). Low HDL or high LDL can cause cholesterol to build up in the arteries, narrowing or blocking blood vessels.
- Triglycerides: The fat in your body that comes from digesting food. High levels of triglycerides can lead to obesity and increase the risk of heart disease.
- C-reactive protein (CRP): A protein produced by the liver that rises during inflammation. Elevated CRP levels can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Lipoprotein(a): A type of lipoprotein similar to LDL, containing cholesterol. High levels of lipoprotein(a) can elevate the risk of cardiovascular disease.
How it works


CHOOSE TEST

COLLECT SAMPLE

GET YOUR RESULTS

You might also like
Genetic Variants and Cardiovascular Disease Risk
There are various genetic variants associated with cardiovascular disease, with some increasing the risk and others offering a protective effect.